Pregnancy-related deaths represent a crucial public health issue, highlighting the alarming rates of maternal mortality in the United States. Recent studies reveal that over 80% of these deaths are preventable, yet the nation continues to lead among high-income countries with a consistently rising mortality rate. Disparities in outcomes persist across various demographic groups, where factors like race and ethnicity contribute significantly to the statistics. The role of cardiovascular disease has become increasingly prominent as a leading cause of these deaths, exacerbating health disparities in postpartum care. Addressing these pregnancy-related deaths calls for urgent policy changes and improved healthcare strategies to ensure equitable maternal health for all women.
The topic of maternal fatalities during pregnancy, often referred to by alternatives such as pregnancy-associated deaths or maternal morbidity, is garnering increasing attention nationwide. Many of these fatalities can be categorized as preventable, shedding light on the urgent necessity for enhanced healthcare systems that address underlying health disparities. The prevalence of chronic conditions, particularly cardiovascular issues, continues to shift the landscape of maternal health, indicating a growing concern for postpartum wellness. Factors surrounding healthcare access, socioeconomic status, and race further complicate the narrative, making it imperative to adopt comprehensive strategies to mitigate these risks. Understanding the variations in maternal health outcomes is crucial for fostering a healthier future for mothers and their families.
Understanding Pregnancy-Related Deaths in the U.S.
Pregnancy-related deaths continue to be a concerning issue in the United States, with alarming statistics indicating that over 80 percent of these fatalities are preventable. The high maternal mortality rate in comparison to other high-income countries raises several questions regarding the effectiveness of the healthcare system and the accessibility of quality maternal care. Studies show that the nation has witnessed a steady increase in pregnancy-related deaths from 2018 to 2022, with a notable spike occurring during the COVID-19 pandemic. Such trends compel us to address the underlying causes of these deaths, focusing on enhancing prenatal care and extending postpartum support to mothers.
Moreover, the disparities in maternal mortality rates are stark, particularly among different racial and ethnic groups. For instance, American Indian and Alaska Native women experience mortality rates that are nearly four times higher than those of their white counterparts. This inequity emphasizes the critical need for targeted interventions within the healthcare system aimed at addressing these health disparities. By prioritizing maternal health through equitable access to quality care and education, it is possible to significantly reduce these tragic outcomes.
The Role of Cardiovascular Disease in Maternal Mortality
Cardiovascular disease has emerged as the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S., contributing to over 20 percent of maternal fatalities. This marks a significant shift from previous decades, where hemorrhage was the primary concern. The rise in cardiovascular-related deaths can be attributed to the increasing prevalence of chronic conditions such as hypertension among pregnant women. As maternal health evolves, it becomes evident that an urgent awareness and proactive management of cardiovascular health during pregnancy are critical in mitigating these risks.
Preventable deaths due to cardiovascular complications underscore the importance of comprehensive prenatal screenings and consistent monitoring for women at risk. Implementing strategies that enhance awareness about the potential risks associated with these conditions can facilitate earlier intervention, which is crucial for improving maternal outcomes. Moreover, healthcare providers must be trained to recognize the signs of cardiovascular illnesses and manage existing chronic conditions effectively, ensuring that mothers can achieve healthier pregnancies and safer deliveries.
Health Disparities Impacting Maternal Health Outcomes
The issue of health disparities in maternal mortality is deeply intertwined with systemic inequalities present in the U.S. healthcare system. Factors such as socioeconomic status, race, and geographic location contribute to the uneven distribution of maternal health resources, leading to stark variations in pregnancy-related health outcomes. For instance, women residing in maternity care deserts face increased risks due to lack of access to essential prenatal and postpartum services. Addressing these disparities is fundamental to ensuring that all mothers receive the care they need and deserve, regardless of their background.
Efforts to combat health disparities must involve a multi-faceted approach that includes policy reform, community-based interventions, and education initiatives designed to empower mothers. By investing in public health infrastructure, particularly in underserved communities, states can work towards creating a more equitable healthcare landscape. Such initiatives could significantly reduce the incidence of preventable pregnancy-related deaths and improve overall maternal health outcomes across diverse populations.
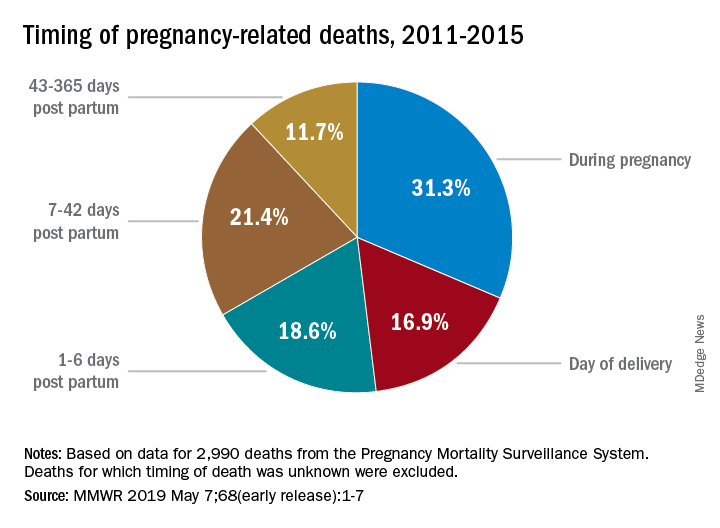
The Importance of Postpartum Care in Reducing Mortality Rates
Postpartum care is a critical component in the continuum of maternal health, significantly impacting the well-being of new mothers. The World Health Organization emphasizes that maternal deaths should be tracked not only during pregnancy but also in the year following childbirth. Late maternal deaths, which occur between 42 days and one year postpartum, represent a significant portion of overall maternal fatalities. This highlights the necessity for enhanced awareness and better healthcare systems that support mothers even after they leave the hospital.
Providing comprehensive postpartum care can help address various complications that may arise during recovery, including mental health issues and chronic conditions exacerbated by pregnancy. By ensuring that follow-up care is prioritized, healthcare providers can identify and mitigate risks early, ultimately reducing the likelihood of maternal mortality. Invested efforts in postpartum health education and resources are essential for empowering mothers to seek help when necessary, thus fostering a supportive environment for recovery.
Navigating the Complexities of Maternal Mortality Data
Accurate tracking of maternal mortality rates in the U.S. has evolved significantly, especially since the implementation of the pregnancy checkbox on death certificates in 2018. This advancement has allowed researchers to gather clearer data on pregnancy-related deaths across the nation, facilitating a better understanding of mortality trends and the factors contributing to these fatalities. The ability to analyze mortality data consistently across states is crucial for identifying areas requiring intervention and crafting effective public health strategies.
However, the challenge remains in addressing the systemic issues that have contributed to maternal mortality data discrepancies. It is vital for policymakers and healthcare providers to collaborate in developing a standardized approach to monitoring maternal health outcomes. By utilizing accurate data, stakeholders can design targeted programs that address the specific needs of affected communities, ultimately leading to more informed decision-making and effective policy implementations.
Investing in Innovative Solutions for Maternal Health
The continued rise in pregnancy-related deaths calls for a reassessment of how healthcare systems allocate resources towards maternal health. Investing in innovative solutions that enhance prenatal and postpartum care delivery is essential to reversing adverse trends. Efforts could include the integration of technology in monitoring maternal health, improved access to telehealth services, and community advocacy programs that educate and empower mothers.
Public health infrastructure investment is also crucial as it provides the foundation for effective maternal health initiatives. By prioritizing funding for research and care models that demonstrate success in lowering maternal mortality rates, stakeholders can create actionable plans that promote healthier pregnancies. This comprehensive approach not only aims to reduce preventable deaths but also seeks to create a sustainable system that supports maternal health long-term.
Racial and Ethnic Disparities in Maternal Health Outcomes
Racial and ethnic disparities in maternal health outcomes remain a pressing issue in the United States, with specific populations experiencing significantly higher rates of pregnancy-related deaths. According to recent studies, American Indian and Alaska Native women, for instance, face mortality rates nearly four times that of white women. This alarming statistic highlights the urgent need for tailored interventions that address the unique challenges faced by marginalized communities within the healthcare system.
To combat these disparities, health systems must implement culturally competent care practices that recognize and respect the diverse backgrounds of patients. Moreover, community outreach programs aimed at educating expectant mothers about available resources and support systems can empower them to navigate their healthcare journeys more effectively. Addressing these disparities not only improves individual health outcomes but also promotes health equity on a broader scale.
The Urgent Need for Policy Reform in Maternal Health
The increasing rates of maternal mortality necessitate immediate policy reform targeting the maternal healthcare system. Policymakers must focus on establishing regulations that address the gaps in care and promote equitable access for all pregnant individuals. This includes advocating for enhanced funding for maternal health programs, ensuring that critical services are available in underserved regions, and promoting maternal health education to expectant parents.
Constructing a more effective maternal health policy framework requires collaboration among healthcare providers, public health officials, and community organizations. By working together, stakeholders can develop comprehensive strategies that target the root causes of maternal mortality and create supportive environments for mothers. Efforts aimed at policy reform should be robustly backed by data, addressing the unique needs and challenges faced by diverse populations in order to facilitate lasting change.
Enhancing Education and Awareness for Maternal Health
Education and awareness play vital roles in empowering pregnant individuals to seek appropriate care and recognize signs of complications. Many women are unaware of the risks associated with pregnancy and childbirth, which can lead to delayed consultations during critical moments. By providing comprehensive education on maternal health, including information on potential pregnancy-related complications, healthcare systems can encourage proactive behaviors that lead to better outcomes.
Community workshops, online resources, and informational campaigns can be effective tools in raising awareness about maternal health issues. Furthermore, it is essential to include educational components that address the socioeconomic and cultural barriers that may prevent women from accessing necessary care. By fostering a community of informed individuals, the likelihood of preventable deaths can be significantly reduced, ultimately enhancing maternal health outcomes nationwide.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is maternal mortality and how does it relate to pregnancy-related deaths?
Maternal mortality refers to the deaths of women during pregnancy or within 42 days of the end of pregnancy due to pregnancy-related issues. It is a critical aspect of pregnancy-related deaths, indicating the safety and quality of healthcare during and after pregnancy.
Why are preventable deaths a significant concern in the context of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S.?
In the U.S., over 80 percent of pregnancy-related deaths are deemed preventable, highlighting critical weaknesses in prenatal and postpartum care. Addressing these preventable deaths is essential to improving maternal health and reducing maternal mortality rates.
How do health disparities affect maternal mortality rates across different racial groups?
Health disparities significantly influence maternal mortality rates, with many studies showing that racial and ethnic minorities, particularly American Indian, Alaska Native, and non-Hispanic Black women, experience disproportionately higher rates of pregnancy-related deaths due to systemic inequities in healthcare access and quality.
What role does postpartum care play in reducing pregnancy-related deaths?
Postpartum care is crucial for preventing pregnancy-related deaths since nearly a third occur postpartum. Improved healthcare during the extended postpartum period can help address complications that arise after childbirth, ultimately reducing maternal mortality rates.
How is cardiovascular disease linked to pregnancy-related deaths?
Cardiovascular disease has emerged as the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths, accounting for over 20%. Conditions like hypertension and cardiac disorders have increasingly affected pregnant women, highlighting the need for better management of pre-existing chronic conditions.
What are the implications of late maternal deaths on overall maternal mortality statistics?
Late maternal deaths, occurring between 42 days and one year postpartum, significantly impact maternal mortality statistics. While they are not included in some definitions, recognizing and addressing these deaths is critical for holistic maternal health care.
What changes have been observed in pregnancy-related deaths among different age groups?
Recent data show that pregnancy-related deaths have risen among women aged 25 to 39, indicating that chronic conditions like hypertension are increasingly affecting younger mothers. This trend necessitates targeted interventions for this age group to improve maternal health.
How can public health infrastructure help reduce pregnancy-related deaths?
Investing in robust public health infrastructure is essential for tracking, understanding, and addressing the root causes of pregnancy-related deaths. Enhanced funding and innovative solutions in maternal care can lead to significant improvements in maternal health outcomes.
What are the challenges in tracking pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S.?
Tracking pregnancy-related deaths has been challenging due to inconsistent methodologies until recently. Implementation of standardized data collection systems in 2018 has improved the ability to monitor and analyze maternal mortality more effectively.
What can be done to improve maternal health outcomes and address pregnancy-related deaths?
Improving maternal health outcomes requires a multi-faceted approach, including greater access to quality prenatal and postpartum care, targeted interventions for high-risk groups, and policies that address systemic healthcare disparities among diverse populations.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Over 80% of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. are preventable. Although the U.S. has high maternal mortality rates, these rates continued to rise from 2018 to 2022, peaking in 2021 during the COVID-19 pandemic. |
| The maternal mortality rate in 2022 was 32.6 deaths per 100,000 live births, up from 25.3 in 2018. |
| Disparities in maternal mortality exist across racial and ethnic groups, with American Indian and Alaska Native women facing the highest rates. |
| Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths, accounting for over 20% of total deaths. |
| Late maternal deaths (after 42 days postpartum) make up nearly a third of total maternal deaths, emphasizing the need for improved postpartum care. |
| Tracking of maternal deaths has improved since 2018 with standardized methods for reporting deaths related to pregnancy. |
| Investment in public health infrastructure and equitable healthcare access is vital to reduce pregnancy-related deaths. |
Summary
Pregnancy-related deaths remain a significant concern in the United States, with alarming statistics showing that over 80% of these deaths are preventable. The rising rates of maternal mortality underscore systemic issues within the healthcare system, which disproportionately affect various racial and ethnic groups. To combat this growing crisis, there is an urgent need for comprehensive healthcare reforms, especially focusing on improving prenatal and postpartum care. Addressing these issues is not only critical for the health and safety of mothers but also essential for future generations.